Introduction
Business Process Management (BPM) tools are software solutions designed to help organizations create, manage, and optimize their business processes. These tools serve as a critical component for businesses looking to streamline complex workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and ensure that every step in a process is executed smoothly. In essence, BPM tools provide a structured framework that enables companies to visualize how work gets done, identify areas of improvement, and implement changes that drive operational efficiency.
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, the need for agility and precision in managing processes has never been greater. Whether it’s a small startup or a large enterprise, every organization relies on a series of interconnected tasks to deliver value to its customers. BPM tools not only facilitate a clearer understanding of these processes but also empower teams to adapt to changes quickly, maintain regulatory compliance, and ultimately achieve strategic goals.
So, how do BPM tools work? By understanding the fundamental principles behind these tools, businesses can unlock their full potential, making informed decisions about which functionalities and features align best with their needs. This blog will delve into the inner workings of BPM tools, providing insights into their key functionalities, types, and real-world benefits.

Overview of BPM Tools
Definition and Purpose
BPM tools are software applications that support the management and optimization of business processes. They enable organizations to design, model, execute, monitor, and refine processes, ensuring that all tasks are aligned with overall business objectives. BPM tools utilize visual workflow diagrams, standardized notations, and automation features to transform complex procedures into easily understandable and manageable sequences of actions.
The primary purpose of BPM tools is to bridge the gap between strategy and execution. By providing a detailed view of processes from start to finish, these tools help identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and bottlenecks. This not only results in smoother operations but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement.
Importance in Business Operations
BPM tools play a crucial role in enabling businesses to visualize, automate, and optimize workflows. At their core, these tools serve as a blueprint for operational efficiency, ensuring that each process step is clearly defined, assigned, and tracked. This level of visibility helps teams stay aligned, reduces the chances of errors, and facilitates better decision-making.
Some of the core benefits include:
- Enhanced Efficiency: BPM tools allow for automation of repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives.
- Cost Reduction: Streamlined processes mean fewer manual interventions and lower operational costs.
- Improved Compliance: By embedding compliance checks and regulatory guidelines directly into workflows, BPM tools help maintain adherence to industry standards and reduce the risk of violations.
In summary, BPM tools are essential for organizations that want to move beyond basic task management and embrace a more strategic, data-driven approach to process optimization. By leveraging their capabilities, businesses can ensure that their workflows are not only effective but also resilient and scalable for future growth.
Key Functionalities of BPM Tools
Process Modeling
Process modeling is the foundation of BPM tools, allowing businesses to map out and document their workflows in a visual format. This is typically achieved using standardized notations such as BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), which provides a consistent way to depict complex processes through flowcharts and symbols. These visual models serve as blueprints that outline every step, decision point, and action in a process, making it easier for all stakeholders to understand and contribute.
Clear process documentation through visual modeling is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps identify inefficiencies and redundancies by providing a holistic view of operations. Second, it serves as a training tool, ensuring that team members have a consistent reference for how tasks should be performed. Finally, it sets the stage for automation and optimization, enabling businesses to create more agile and adaptable workflows.
Automation
One of the most powerful aspects of BPM tools is their ability to automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks. By configuring predefined rules and triggers, organizations can ensure that mundane tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, generating reports, or approving routine requests, are executed automatically without manual intervention. This automation capability not only speeds up processes but also minimizes the risk of human error, resulting in higher accuracy and consistency.
The benefits of automation in BPM are manifold. First, it significantly reduces the time required to complete tasks, leading to faster turnaround times and higher productivity. Second, it eliminates the need for constant oversight, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-adding activities. Lastly, automation ensures that processes are executed the same way every time, maintaining quality and compliance across the board.
Monitoring and Analytics
BPM tools come equipped with robust monitoring and analytics features that provide real-time insights into process performance. Through interactive dashboards and visual reports, users can track key metrics such as task completion times, resource utilization, and process efficiency. This level of visibility is essential for identifying bottlenecks, delays, or any deviations from the intended workflow.
The ability to monitor processes in real-time is invaluable for businesses aiming to optimize their operations continuously. Analytics can highlight areas where performance is lagging, enabling teams to pinpoint and address root causes quickly. Moreover, by leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can make informed decisions about process adjustments, ensuring that workflows remain agile and aligned with evolving business needs.
Collaboration
Effective collaboration is a cornerstone of successful process management, and BPM tools facilitate this through features designed to enhance teamwork and communication. These tools often include shared workspaces, task assignment capabilities, and real-time notifications, allowing team members to stay informed and aligned as they work through different stages of a process.
For example, a BPM tool might enable a project manager to assign tasks, set deadlines, and track the progress of multiple contributors in a centralized dashboard. Team members can leave comments, share files, and request clarifications within the same interface, ensuring smooth handoffs and reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings. Such collaborative features are particularly valuable in complex projects involving cross-functional teams, as they promote transparency and foster a culture of accountability.
Integration
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, no BPM tool can operate in isolation. Effective BPM tools are designed to integrate seamlessly with an organization’s existing IT infrastructure, connecting with other software applications such as CRM systems, ERP platforms, and document management systems. This ensures that data flows smoothly between systems, eliminating silos and enabling a unified view of business operations.
Seamless integration capabilities are essential for maintaining process continuity across different platforms. For instance, a BPM tool might pull customer data from a CRM, process it through an approval workflow, and then update the information in a document management system—all without manual input. This not only saves time but also ensures that data remains accurate and up-to-date across all touchpoints, supporting more informed decision-making and smoother operations.
Types of BPM Tools
BPM tools can be categorized based on their primary focus and the specific needs they address. Understanding these types helps organizations choose the right tool that aligns with their operational goals and existing infrastructure.
Human-Centric BPM
Human-Centric BPM tools are designed with a strong emphasis on user involvement, making them ideal for processes that require frequent human interaction and decision-making. These tools support dynamic task assignments, where users can delegate, prioritize, and reassign tasks as needed. Human-centric BPM tools often include user-friendly interfaces, collaborative features, and role-based access controls to ensure smooth communication and task management across teams.
This type of BPM is particularly beneficial in scenarios where approvals, feedback loops, or hands-on collaboration are essential, such as project management, customer support, or human resource workflows. By placing users at the center of the process, these tools facilitate flexibility and adaptability in rapidly changing environments.
Document-Centric BPM
Document-Centric BPM tools focus primarily on managing the flow of documents and information within business processes. These tools are equipped with robust document management capabilities, including version control, secure storage, and document routing. They are ideal for organizations that handle large volumes of both physical and digital documents, such as legal firms, finance departments, and healthcare providers.
The primary goal of document-centric BPM tools is to streamline document handling and reduce the risk of errors or lost files. By automating the approval, review, and archival of documents, these tools ensure that critical information is processed efficiently and securely, enhancing compliance and traceability.
Integration-Centric BPM
Integration-Centric BPM tools are designed to connect various software applications within an organization’s IT ecosystem, enabling smooth data exchange and process continuity. These tools are typically used for processes that span multiple systems, such as supply chain management or order processing, where data from different sources needs to be synchronized and updated in real-time.
Integration-centric BPM tools excel at creating seamless workflows between disparate platforms like CRMs, ERPs, and other business applications. By ensuring that these systems communicate effectively, these tools help eliminate data silos, reduce manual data entry, and support more cohesive and streamlined operations.
Key Features to Look For in BPM Tools
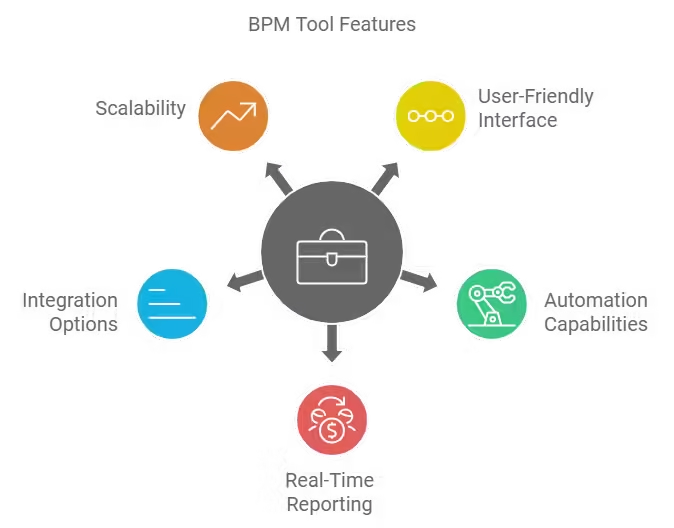
When evaluating BPM tools, it’s essential to consider specific features that align with the organization’s needs. These features not only enhance the tool’s usability but also determine its effectiveness in optimizing processes.
User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly interface is crucial for ensuring that the BPM tool is accessible to all users, regardless of their technical expertise. Look for a tool that offers an intuitive visual workflow builder, drag-and-drop functionality, and clear process visualizations. A simple yet powerful interface minimizes the learning curve, making it easier for teams to create, modify, and deploy workflows without requiring extensive training or IT support.
Automation Capabilities
Automation is at the heart of any effective BPM tool. The tool should offer robust automation features that allow users to automate repetitive tasks, set up rule-based triggers, and create automated workflows. This not only enhances efficiency by speeding up task completion but also ensures consistency and accuracy by reducing the potential for human error. Key automation features to consider include task scheduling, notifications, and automated approvals.
Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Real-time reporting and analytics are essential for gaining visibility into process performance. The BPM tool should provide interactive dashboards and visual reports that display key metrics such as task completion times, process bottlenecks, and resource utilization. These insights enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, quickly identify areas for improvement, and optimize processes to achieve better outcomes.
Integration Options
BPM tools need to integrate seamlessly with other software solutions used within the organization to facilitate data sharing and process continuity. Look for tools that offer built-in connectors, APIs, or plug-ins for popular business applications like CRM, ERP, and document management systems. Effective integration options prevent data silos, streamline workflows, and enable end-to-end process management across different platforms.
Scalability
Scalability is a key consideration for growing organizations. A BPM tool should be able to accommodate more complex processes as the business expands, supporting increased user numbers, more sophisticated workflows, and additional automation rules. The tool’s architecture should be flexible enough to handle larger volumes of data and adapt to evolving business needs without compromising performance.
By prioritizing these key features, businesses can select a BPM tool that not only meets their current requirements but also positions them for future growth and success.
Benefits of Using BPM Tools
Implementing Business Process Management (BPM) tools can provide organizations with numerous advantages that go beyond simple task management. From boosting efficiency to enhancing customer satisfaction, BPM tools empower businesses to operate at their highest potential. Here’s a closer look at the primary benefits of adopting BPM tools.
Increased Efficiency
BPM tools significantly enhance organizational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing complex workflows. Automation minimizes the need for manual intervention, allowing employees to focus on high-priority activities that require human judgment and creativity. Moreover, by providing a clear visual representation of processes, BPM tools help identify and eliminate redundant steps, leading to more streamlined and agile operations.
The impact on productivity can be profound, as tasks that previously took hours to complete can be executed in minutes. This increased efficiency not only speeds up service delivery but also ensures that resources are used more effectively, contributing to overall business growth.
Cost Reduction
One of the most tangible benefits of using BPM tools is the reduction in operational costs. By automating routine tasks and minimizing errors, organizations can lower costs associated with manual labor, rework, and inefficiencies. Additionally, streamlined processes mean that fewer resources are needed to achieve the same, or even better, results.
For example, a BPM tool can automate the approval process for expense reports, reducing the time employees spend on administrative work. Similarly, optimizing supply chain workflows can result in lower inventory costs and decreased lead times. These cost savings accumulate over time, improving the organization’s bottom line.
Improved Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a major concern for businesses operating in industries with strict standards, such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. BPM tools help ensure compliance by embedding regulatory requirements and audit trails directly into workflows. This means that every step of a process can be monitored, documented, and verified against compliance criteria.
With features like role-based access controls, automated document handling, and compliance checklists, BPM tools provide a structured approach to maintaining adherence to industry regulations. This not only reduces the risk of costly compliance breaches but also provides peace of mind, knowing that processes are being executed in accordance with legal and regulatory standards.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
BPM tools play a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction by enabling faster response times and improving the quality of service delivery. By automating routine interactions and optimizing back-end processes, businesses can respond to customer inquiries more quickly and accurately. Furthermore, streamlined workflows ensure that customer-facing processes—such as order management, service requests, and issue resolution—are handled efficiently and consistently.
This improved agility and responsiveness lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, as clients experience fewer delays, faster resolutions, and a more personalized service experience. In today’s competitive landscape, such enhancements can be a key differentiator, setting the business apart from its competitors.
By leveraging these benefits, organizations can drive operational excellence, reduce costs, and deliver superior value to both customers and stakeholders.
How BPM Tools Work – A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Understanding how BPM tools function can demystify their role in transforming business processes. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how these tools are typically used to design, implement, and optimize workflows within an organization.
Step 1: Process Design and Modeling
The first stage involves designing and modeling the business processes using visual tools and standardized notations like BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation). This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the entire workflow, allowing stakeholders to map out each task, decision point, and data flow clearly.
During process modeling, the organization identifies every step involved in a workflow and establishes a logical sequence for task completion. The visual representation helps teams understand how work is carried out, highlighting dependencies and pinpointing inefficiencies. This clarity sets the stage for successful process implementation and ensures that every aspect of the workflow is well-documented.
Step 2: Automation and Implementation
Once the process design is finalized, the next step is to implement automation rules and logic within the BPM tool. Automation involves configuring tasks to be executed automatically based on predefined triggers and conditions. For instance, an approval workflow can be set to automatically route documents to the appropriate manager when certain criteria are met.
This step reduces the need for manual intervention, speeding up the workflow and minimizing human error. Automation can include simple tasks like sending notifications or more complex actions such as data validation, cross-system updates, and dynamic task allocation. The implementation of these automated rules ensures that the process runs smoothly and consistently every time.
Step 3: Monitoring and Optimization
After automation is set up, the BPM tool allows for real-time monitoring of process performance. Dashboards and analytics features track key metrics such as task completion times, resource usage, and potential bottlenecks. This ongoing monitoring is crucial for maintaining process efficiency and identifying areas for improvement.
Using insights gained from the monitoring phase, teams can optimize processes by making adjustments to workflows, reallocating resources, or modifying automation rules. This continuous improvement cycle helps organizations respond to changing business needs and maintain high levels of performance and productivity.
Step 4: Collaboration and Refinement
Collaboration is a critical aspect of process management, and BPM tools provide various features that facilitate teamwork and communication. At this stage, team members can use shared workspaces, comment threads, and task management tools to refine workflows based on real-time feedback and performance data.
For example, if a bottleneck is identified in a particular step, the team can discuss and implement a solution, such as reassigning tasks or adjusting deadlines. This collaborative approach ensures that all stakeholders are involved in process refinement, promoting continuous improvement and alignment across departments.
Step 5: Integration and Scalability
The final stage involves ensuring that the BPM tool integrates seamlessly with the organization’s existing IT infrastructure. Effective integration allows for smooth data flow between various systems such as CRMs, ERPs, and project management tools, enabling a unified view of business operations.
Additionally, the BPM tool should be scalable to accommodate future growth. This means that as the organization expands and its processes become more complex, the BPM tool can support more users, additional workflows, and increased data volumes without compromising performance. Scalability ensures that the BPM tool remains a long-term solution that evolves with the business.
By following these steps, organizations can fully leverage the power of BPM tools to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and achieve strategic goals.
Conclusion
Business Process Management (BPM) tools are transformative solutions that enable organizations to design, automate, monitor, and refine their workflows for optimal efficiency and effectiveness. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored how BPM tools work step-by-step, covering their core functionalities such as process modeling, automation, monitoring, collaboration, and integration. By visualizing complex processes, automating repetitive tasks, and providing real-time insights, BPM tools empower businesses to operate more smoothly, reduce costs, and maintain compliance.
The benefits of implementing BPM tools are substantial: they drive increased productivity, support cost-effective operations, and enhance overall service quality. For any business aiming to remain competitive and agile in a rapidly evolving marketplace, BPM tools are an invaluable asset. They not only streamline day-to-day operations but also lay the groundwork for continuous improvement and long-term success.
If your organization is looking to optimize its processes, now is the perfect time to explore the potential of BPM tools. Whether you need to automate workflows, improve team collaboration, or ensure compliance, choosing the right BPM solution can be a game-changer. Start by evaluating your current processes and considering which functionalities and features will best support your strategic goals.
References
The information and insights provided in this blog are supported by detailed research from the following resources:
- Cflow Apps
- Nected AI
- Filestage
- TechTarget
- GitHub – Awesome BPM
- MEGA International
- BeSlick
- Gartner Reviews
These sources offer additional insights and detailed comparisons of BPM tools, making them a valuable starting point for anyone looking to dive deeper into Business Process Management.
FAQ
- What are BPM tools, and how do they differ from project management tools?
BPM (Business Process Management) tools are designed specifically to map, automate, and optimize business processes, while project management tools focus on planning and executing individual projects. BPM tools provide a holistic view of workflows and ensure that each step in a process is executed efficiently, whereas project management tools are more about task tracking and resource allocation for specific projects. - Can BPM tools be customized for unique business needs?
Yes, most BPM tools are highly customizable. They offer flexible process modeling, configurable automation rules, and integration capabilities, allowing businesses to tailor workflows to their specific requirements. This adaptability makes BPM tools suitable for a wide range of industries and business scenarios. - What types of businesses benefit the most from using BPM tools?
Any organization with complex, repetitive processes can benefit from BPM tools. This includes industries such as finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and customer service. Businesses that need to maintain regulatory compliance, improve process visibility, or enhance collaboration across teams are prime candidates for BPM solutions. - Are BPM tools difficult to implement and use?
Modern BPM tools are designed to be user-friendly, often featuring drag-and-drop interfaces and visual workflow builders. However, the complexity of implementation depends on the size of the organization and the intricacy of its processes. Many BPM tools also offer comprehensive support and training to ease the transition. - How do I choose the right BPM tool for my organization?
Start by evaluating your current processes and identifying the specific challenges you want to address, such as automation, compliance, or integration needs. Look for BPM tools that offer key features like ease of use, strong integration capabilities, real-time monitoring, and scalability to ensure it aligns with your business goals and future growth. Conduct trials and consult reviews to find the best fit for your organization.